Overview
The prerequisites for this tutorial are that MySQL has already been installed and that a database has been created. The database name in these examples will be mcs.
A Quality test can only be performed by an Access Device. Any MySpeed or MyHiSpeed test run from an Access Device will output results to the Quality database.
Create Table
The CREATE TABLE statement below can be used to create a table named quality. The table includes some generic test metrics, such as ISP, IP and Session ID (SID), along with the results of the test.
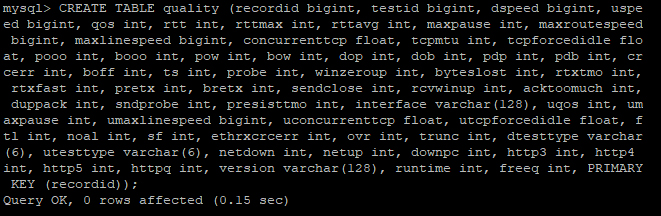
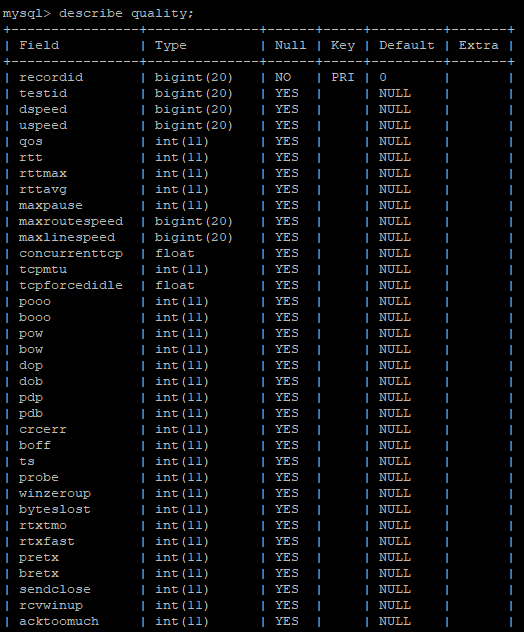
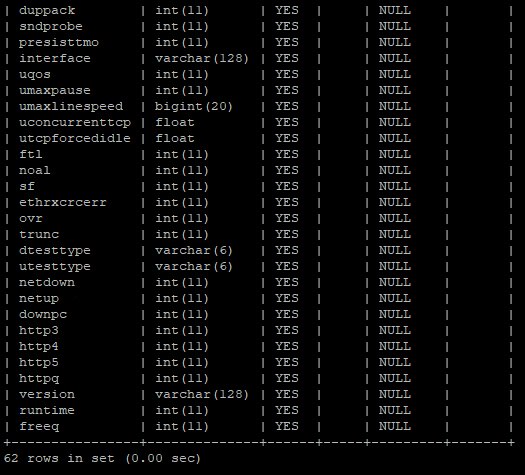
CREATE TABLE quality (recordid bigint, testid bigint, dspeed bigint, uspeed bigint, qos int, rtt int, rttmax int, rttavg int, maxpause int, maxroutespeed bigint, maxlinespeed bigint, concurrenttcp float, tcpmtu int, tcpforcedidle float, pooo int, booo int, pow int, bow int, dop int, dob int, pdp int, pdb int, crcerr int, boff int, ts int, probe int, winzeroup int, byteslost int, rtxtmo int, rtxfast int, pretx int, bretx int, sendclose int, rcvwinup int, acktoomuch int, duppack int, sndprobe int, presisttmo int, interface varchar(128), uqos int, umaxpause int, umaxlinespeed bigint, uconcurrenttcp float, utcpforcedidle float, ftl int, noal int, sf int, ethrxcrcerr int, ovr int, trunc int, dtesttype varchar(6), utesttype varchar(6), netdown int, netup int, downpc int, http3 int, http4 int, http5 int, httpq int, version varchar(128), runtime int, freeq int, PRIMARY KEY (recordid));The image below is an example of copying and pasting the above statement into a MySQL command prompt. Once the table has been created, the describe tablename; command can be used to view the newly created table structure.
Enable MySQL
The next step is to enable MySQL in MyConnection Server (MCS). This step may have already been done. If not, click here.
Create Profile
With MySQL enabled and the table created, configure MCS to export data. The first step is to create a SQL profile.
From the MCS main menu, click Manage SQL Profiles in the administration panel.
On the resulting page, click Create new SQL profile.
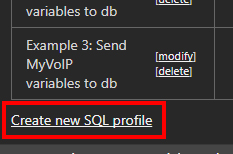
The first step when creating a new profile is to enter the connection settings:
- Name: Enter a name for the profile. This will appear in the list of profiles on the previous page.
- Server Type & Address: Select MySQL from the dropdown and enter the IP/domain and port number of the MySQL database.
- Credentials & DB: Enter the login credentials for the MySQL server and the database name that contains the table created in the first part of this tutorial.
- Run: Check the Run... box. With this box checked, the SQL profile will run each time a Speed test is run, ensuring all data gets exported.
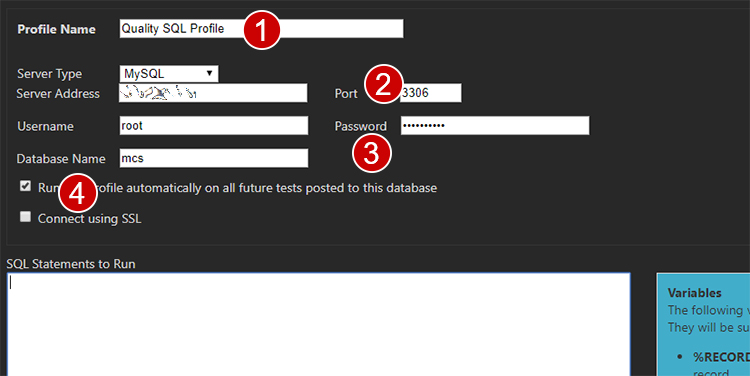
Save the profile, which will return to the profiles list. Immediately modify the profile, as the next step is defining the export data.
Define Export Data
The SQL Statements to run text box is where the export data is specified, in the form of an INSERT INTO statement.
The INSERT INTO statement below matches the CREATE TABLE specified in the first step. Copy and paste it into the text box.
[act] INSERT INTO quality (recordid, testid, dspeed, uspeed, qos, rtt, rttmax, rttavg, maxpause, maxroutespeed, maxlinespeed, concurrenttcp, tcpmtu, tcpforcedidle, pooo, booo, pow, bow, dop, dob, pdp, pdb, crcerr, boff, ts, probe, winzeroup, byteslost, rtxtmo, rtxfast, pretx, bretx, sendclose, rcvwinup, acktoomuch, duppack, sndprobe, presisttmo, interface, uqos, umaxpause, umaxlinespeed, uconcurrenttcp, utcpforcedidle, ftl, noal, sf, ethrxcrcerr, ovr, trunc, dtesttype, utesttype, netdown, netup, downpc, http3, http4, http5, httpq, version, runtime, freeq) VALUES (%RECORDID%, %TESTID%, %ACT.DSPEED%, %ACT.USPEED%, %ACT.QOS%, %ACT.RTT%, %ACT.RTTMAX%, %ACT.RTTAVG%, %ACT.MAXPAUSE%, %ACT.MAXROUTESPEED%, %ACT.MAXLINESPEED%, %ACT.CONCURRENTTCP%, %ACT.TCPMTU%, %ACT.TCPFORCEDIDLE%, %ACT.TCPRXPOOO%, %ACT.TCPRXBOOO%, %ACT.TCPRXPOW%, %ACT.TCPRXBOW%, %ACT.TCPRXDOP%, %ACT.TCPRXDOB%, %ACT.TCPRXPDP%, %ACT.TCPRXPDB%, %ACT.TCPRXCRCERR%, %ACT.TCPRXBOFF%, %ACT.TCPRXTS%, %ACT.TCPRXPROBE%, %ACT.TCPRXWINZEROUP%, %ACT.TCPBYTESLOST%, %ACT.TCPTXRTXTMO%, %ACT.TCPTXRTXFAST%, %ACT.TCPTXPRETX%, %ACT.TCPTXBRETX%, %ACT.TCPTXSNDWINCLOSE%, %ACT.TCPTXRCVWINUPD%, %ACT.TCPTXRCVACKTOOMUCH%, %ACT.TCPTXRCVDUPACK%, %ACT.TCPTXSNDPROBE%, %ACT.TCPTXPERSISTTIMEO%, '%ACT.INTERFACE%', %ACT.UQOS%, %ACT.UMAXPAUSE%, %ACT.UMAXLINESPEED%, %ACT.UCONCURRENTTCP%, %ACT.UTCPFORCEDIDLE%, %ACT.ETHRXFTL%, %ACT.ETHRXNOAL%, %ACT.ETHRXSF%, %ACT.ETHRXCRCERR%, %ACT.ETHRXOVR%, %ACT.ETHRXTRUNC%, '%ACT.DTESTTYPE%', '%ACT.UTESTTYPE%', %ACT.NETDOWNSEC%, %ACT.NETUPSEC%, %ACT.NETDOWNPC%, %ACT.HTTP3XXSEC%, %ACT.HTTP4XXSEC%, %ACT.HTTP5XXSEC%, %ACT.HTTPQXXSEC%, '%ACT.VERSION%', %ACT.RUNTIME%, %ACT.FREEQ%);Once pasted, it should look like this:
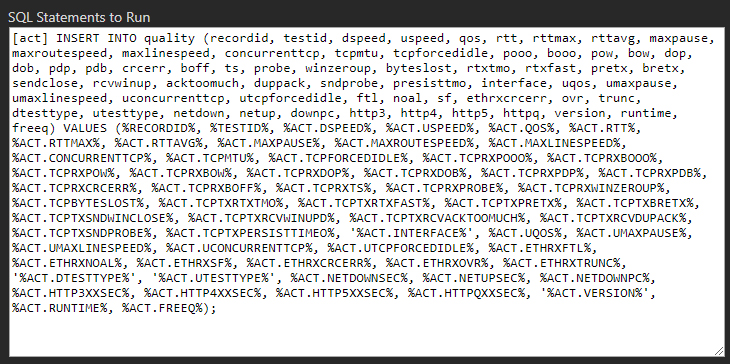
Save the profile to complete the process.
Now, whenever a Quality test is run, this MySQL export should run and put data in the database.
When using a MySQL command prompt, the data for a table can be viewed by using the command select * from tablename.

