Overview
Security settings for MyConnection Server (MCS) can be found by clicking the
Two-Factor Authentication
Since version 11.3a, MCS has supported two-factor authentication (2FA) via email. 2FA is an extra layer of security to verify that users trying to access an account are who they claim to be.
When new users are created in MCS, an email address is required. This email address is used to deliver the 2FA OTP code.
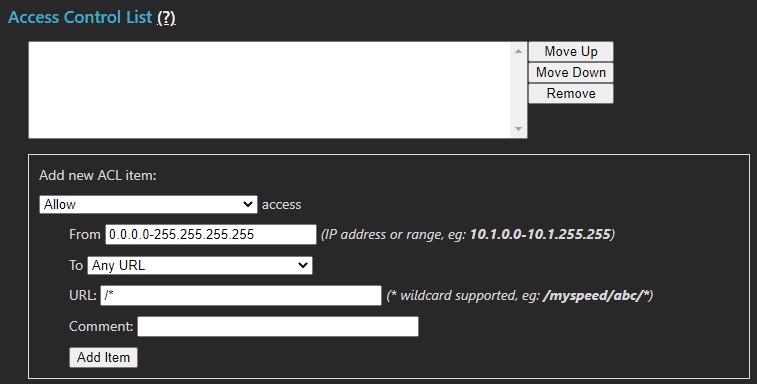
Access Control List (ACL)
The ACL controls access permissions to all or part of MCS. Restrictions can be applied by feature and by IP address, including ranges and subnets. The list defines what is permitted or denied, processed in order — the first matching rule is applied. If no rule matches, the URL is allowed subject to MCS roles.
Warning: Be careful with blanket deny rules, as they can block complete access to MCS.
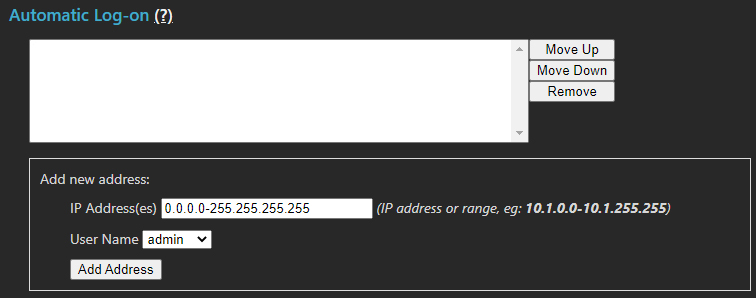
Automatic Log-on
Workstations can be automatically logged on based on IP address. The list below defines the IP addresses configured for auto-logon. Workstations can still log in as a different user if extended privileges are required.
Warning: Using auto-logon for administrative privilege users is not advised.
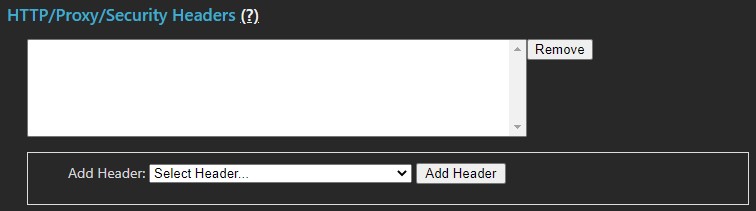
Security Headers
Security headers allow the MCS administrator to add specific external headers to MCS HTTP transactions. Add custom headers using the Custom Header text field or choose from a list of common headers.
Warning: MCS is a custom web service application, not a commercial web server such as IIS or Apache. Adding headers may invoke restrictions that affect overall MCS service delivery.
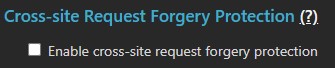
Cross-Site Forgery (CSRF)
Cross-site forgery request attacks can allow a user to unwittingly submit a form or click a URL hosted on a malicious site that targets MCS. Enabling this option requires all future administrative access to be performed using forms submitted from MCS. If an MCS URL is referred from outside the MCS domain, the request is blocked as a CSRF violation and the requester is redirected correctly.
Cookie Attributes
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable Secure | If MCS is deployed behind a proxy (e.g., Apache) that serves it via HTTPS, MCS will add the secure attribute to the Set-Cookie header. |
| Enable httponly | Restricts Java applets from obtaining MCS session cookies from the browser. If enabled, ensure that the MCS applet testing option is enabled for the "public" user, otherwise browser-based testing will be permanently disabled. |

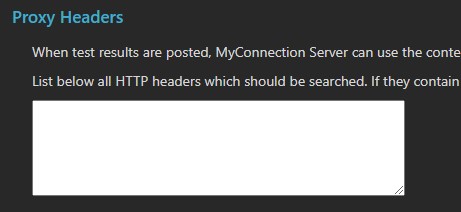
Proxy Headers
Proxy services can interfere with correct IP identification of clients. MCS provides proxy header settings to allow the contents of an HTTP header to specify the public IP address for accurate user identification.
Token Passcodes (TPS)
Token passcodes are not passwords — TPS provides encryption services for satellite and other test protocol requests.
| Passcode | Description |
|---|---|
| Work Order Passcode | Before any satellite can initiate a test to an MCS, NQC Server, or Satellite Access server, the work order must first authenticate using this passcode. |
| NQC Client Passcode | Licensed NQC client apps for mobile phones and tablets (iPhone, Android) are required to authenticate using this passcode. |
| Database Post Password | Deprecated. Replicating MCS database results to another MCS requires this passcode on the receiving MCS. |
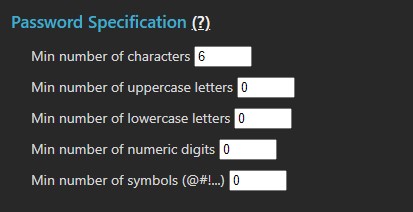
Password Specification
User password rules define the complexity requirements for all user passwords in MCS. These rules do not apply to MCS passcode tokens listed above.
Route Testing (IPv4 Only, Deprecated)
IP rules define addresses that cannot appear within any route table or be allowed as a route destination. Enter one IP per line or an IP range (e.g., 10.0.0.0-10.255.255.255).
Custom alias names can be declared for specific IP addresses using the format IP=<alias name>. For example: 10.0.0.0=myprivate_server.